Resources
The Resources tab provides visibility into cloud infrastructure metrics for your PostgreSQL deployment. Currently, this tab supports AWS RDS metrics via CloudWatch integration.
Note: This tab is only available when the deployment type is set to "RDS" in configuration.
Sections
The Resources tab is organized into four sections:
- CPU — CPU utilization and load metrics
- Memory — Available memory tracking
- Disk — Storage and I/O metrics
- Network — Throughput monitoring
CPU Section
The CPU section provides insight into processor utilization across your RDS cluster.
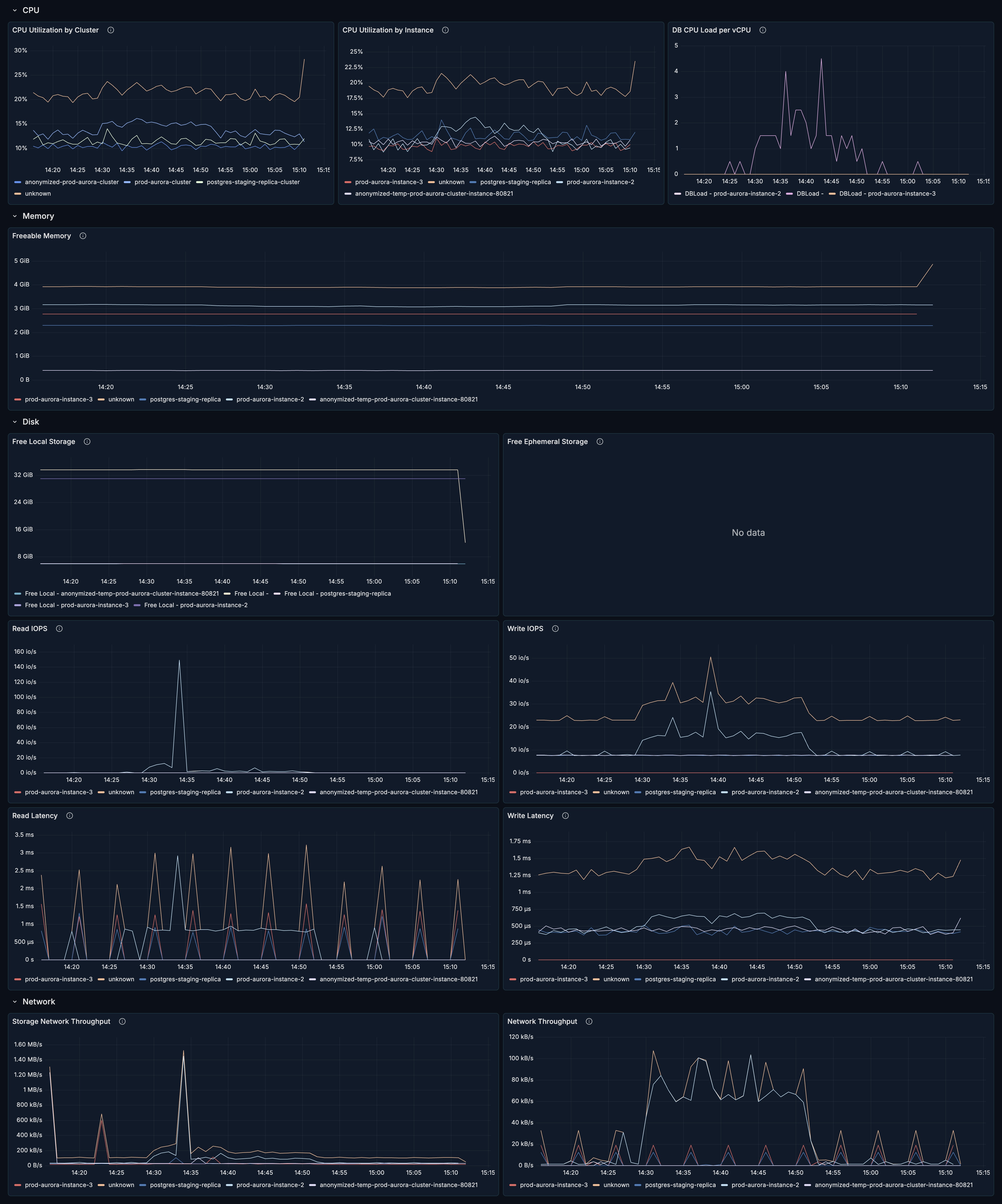
CPU Utilization by Cluster
What it shows: Aggregate CPU utilization across all instances in the cluster.
Healthy range: < 70% for sustained workloads.
When to investigate:
- Sustained > 70% — consider scaling up
- Spikes to 100% — identify resource-intensive queries
- Sudden changes — correlate with application behavior
CPU Utilization by Instance
What it shows: CPU utilization per database instance.
How to use it:
- Identify hot instances
- Compare primary vs replica load
- Detect uneven load distribution
Healthy pattern:
- Primary slightly higher than replicas
- Even distribution across read replicas
- Predictable patterns matching traffic
DB CPU Load per vCPU
What it shows: Database load normalized per vCPU.
Interpretation:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| < 1.0 | CPU has capacity |
| = 1.0 | CPU fully utilized |
| > 1.0 | Queries waiting for CPU |
When to investigate:
- Load > 1.0 — CPU bottleneck
- Growing trend — scaling needed
- Spikes — resource-intensive queries
Memory Section
The Memory section tracks available memory on your RDS instances. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.
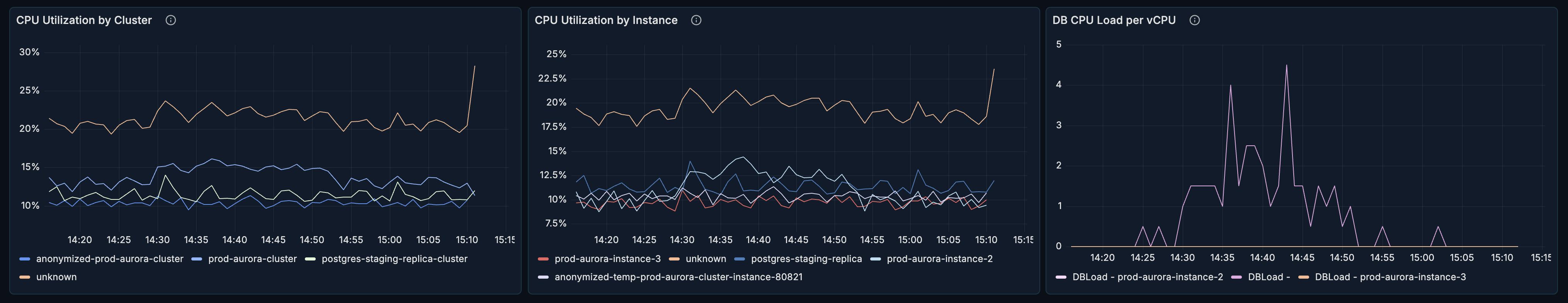
Freeable Memory
What it shows: Amount of RAM available on the instance.
Healthy range: > 20% of total instance memory.
When to investigate:
- Dropping below 20% of total
- Consistent decline over time
- Correlation with slow queries
Low memory causes:
shared_bufferstoo largework_memtoo large for concurrent queries- Memory leaks in extensions
- Too many connections
Optimization tips:
- Review PostgreSQL memory settings
- Consider instance upgrade
- Optimize connection pooling
- Check for memory-intensive queries
Disk Section
The Disk section monitors storage capacity and I/O performance. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.

Free Local Storage
What it shows: Available local SSD storage.
Usage:
- Temporary files
- Sort operations
- Hash operations
When to investigate:
- Running low on space
- Rapid consumption during queries
- Correlation with slow queries
Free Ephemeral Storage
What it shows: Available ephemeral storage.
Note: Not all instance types have ephemeral storage.
Read IOPS
What it shows: Read I/O operations per second.
What affects it:
- Query volume
- Buffer cache misses
- Table scan operations
- Index usage patterns
When to investigate:
- Approaching provisioned IOPS limit
- Sudden spikes
- Sustained high levels
Write IOPS
What it shows: Write I/O operations per second.
What affects it:
- Transaction volume
- WAL writes
- Checkpoint activity
- Background writer
When to investigate:
- Approaching provisioned IOPS limit
- Spikes during maintenance
- Correlation with lag
Read Latency
What it shows: Average time for read operations.
Healthy range: < 10ms for most workloads.
When to investigate:
- Latency > 20ms
- Increasing trend
- Correlation with query slowness
High latency causes:
- IOPS throttling
- Storage system issues
- Network congestion
Write Latency
What it shows: Average time for write operations.
Healthy range: < 10ms for most workloads.
When to investigate:
- Latency > 20ms
- Increasing trend
- Correlation with transaction slowness
Network Section
The Network section monitors data transfer metrics. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.
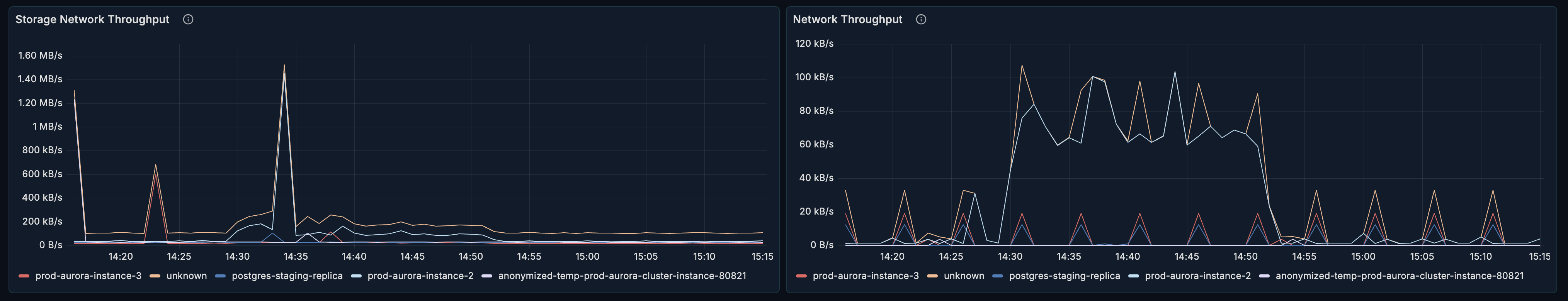
Storage Network Throughput
What it shows: Data transfer rate to/from storage.
What affects it:
- Query data volume
- Backup operations
- Large data transfers
When to investigate:
- Approaching network limits
- Correlation with performance issues
- Unexpected spikes
Network Throughput
What it shows: Overall network data transfer rate.
What affects it:
- Client traffic
- Replication traffic
- Application data transfer
When to investigate:
- Bandwidth saturation
- Unexpected traffic patterns
- Correlation with timeouts
Use Cases
Performance Troubleshooting
When experiencing slow queries:
- Check CPU Utilization — is CPU a bottleneck?
- Review DB CPU Load per vCPU — load > 1.0 indicates CPU queueing
- Check Read/Write IOPS — are you hitting IOPS limits?
- Review Read/Write Latency — is storage slow?
- Check Freeable Memory — is memory pressure causing issues?
Capacity Planning
For scaling decisions:
- Track CPU Utilization trends over time
- Monitor DB CPU Load per vCPU for headroom
- Review IOPS consumption vs provisioned
- Check Freeable Memory trends
- Analyze Network Throughput for bandwidth needs
Scaling indicators:
- Sustained CPU > 70%
- DB Load > 0.7 consistently
- IOPS > 80% of provisioned
- Memory < 20% available
- Latency increasing trend
Instance Right-Sizing
To optimize costs:
- Review CPU Utilization — consistently low may indicate over-provisioning
- Check Freeable Memory — excess memory is wasted cost
- Analyze IOPS patterns — may allow reduced provisioning
- Consider workload patterns — can you use smaller instances off-peak?
Monitoring During Maintenance
During maintenance windows:
- Watch Write IOPS during vacuums
- Monitor CPU during REINDEX
- Track Freeable Memory during bulk operations
- Check Latency for impact on operations
AWS RDS Metrics Reference
The Resources section uses CloudWatch metrics:
| Panel | CloudWatch Metric |
|---|---|
| CPU Utilization (Cluster) | CPUUtilization (aggregated) |
| CPU Utilization (Instance) | CPUUtilization (per instance) |
| DB CPU Load | DBLoadCPU |
| Freeable Memory | FreeableMemory |
| Free Local Storage | FreeLocalStorage |
| Free Ephemeral Storage | FreeEphemeralStorage |
| Read IOPS | ReadIOPS |
| Write IOPS | WriteIOPS |
| Read Latency | ReadLatency |
| Write Latency | WriteLatency |
| Storage Throughput | StorageNetworkThroughput |
| Network Throughput | NetworkThroughput |
Configuration
To enable the Resources section:
- Set Deployment Type to "rds" in pgX configuration
- Configure CloudWatch metrics collection
- Set RDS Service Name and Metrics Prefix
See Configuration Reference for details.
Related Guides
- Performance — Query performance analysis
- Connections — Connection pool management
- Configuration Reference — RDS configuration options