Locks & Waits
The Locks & Waits tab provides visibility into PostgreSQL concurrency behavior. Use it to identify lock contention, detect deadlocks, analyze blocking sessions, and troubleshoot wait events.
Sections
The Locks & Waits tab is organized into four sections:
- Concurrency Overview — Lock types and deadlock monitoring
- Locks Grid — Detailed view of all locks
- Blocking Analysis — Blocking chains and impact assessment
- Wait Event Analysis — PostgreSQL wait event distribution
Concurrency Overview Section
The Concurrency Overview section provides immediate visibility into lock activity.
Lock Count by Type
A pie chart showing the distribution of lock types.
Lock types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| relation | Table-level locks |
| tuple | Row-level locks |
| transactionid | Transaction ID locks |
| virtualxid | Virtual transaction ID locks |
| object | Database object locks |
| userlock | User-defined advisory locks |
| advisory | Advisory locks |
Healthy pattern:
- Mostly relation and transactionid locks
- Few tuple locks (row-level contention)
- Advisory locks if using application locking
When to investigate:
- High tuple lock count — row contention
- Growing lock counts — possible lock escalation
- Unexpected lock types — review application behavior
Lock Wait Queue Depth
What it shows: Number of sessions waiting for locks over time.
Healthy range: Near zero for most workloads.
When to investigate:
- Queue depth > 0 sustained
- Growing trend
- Spikes correlating with slowness
High queue causes:
- Long-running transactions
- Lock contention on hot rows
- Missing indexes causing table locks
Deadlock Frequency
What it shows: Number of deadlocks over time.
Healthy range: Zero.
When to investigate:
- Any deadlocks occurring
- Recurring patterns
- Increasing frequency
Deadlock causes:
- Circular lock dependencies
- Inconsistent lock ordering
- Long transactions increasing collision probability
Locks Grid Section
The Locks Grid shows detailed information about all current locks. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.
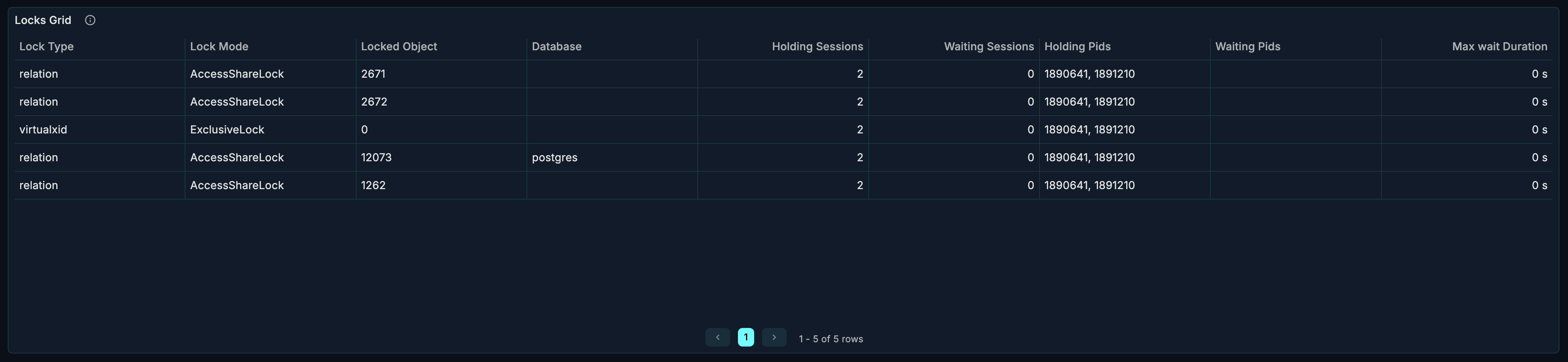
Table Columns
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| PID | Backend process ID |
| Database | Database name |
| Lock Type | Type of lock held/requested |
| Mode | Lock mode (AccessShare, RowExclusive, etc.) |
| Granted | Whether lock is held (true) or waiting (false) |
| Relation | Table or object being locked |
| Wait Start | When waiting began |
Lock Modes
| Mode | Description | Conflicts With |
|---|---|---|
| AccessShareLock | SELECT | AccessExclusiveLock |
| RowShareLock | SELECT FOR UPDATE | Exclusive, AccessExclusive |
| RowExclusiveLock | UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT | Share, ShareRowExclusive, Exclusive, AccessExclusive |
| ShareUpdateExclusiveLock | VACUUM, ANALYZE | ShareUpdateExclusive, Share, ShareRowExclusive, Exclusive, AccessExclusive |
| ShareLock | CREATE INDEX | RowExclusive, ShareUpdateExclusive, ShareRowExclusive, Exclusive, AccessExclusive |
| ShareRowExclusiveLock | Rarely used | RowExclusive, ShareUpdateExclusive, Share, ShareRowExclusive, Exclusive, AccessExclusive |
| ExclusiveLock | Blocks reads/writes | All except AccessShare |
| AccessExclusiveLock | ALTER TABLE, DROP | All |
How to Use
Find blocked sessions:
- Filter for Granted = false
- These sessions are waiting for locks
Identify blockers:
- Find locks on same relation
- Match PIDs with Granted = true
Track wait duration:
- Check Wait Start timestamp
- Long waits indicate serious contention
Blocking Analysis Section
The Blocking Analysis section helps identify blocking chains and their impact. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.
Blocking Sessions Node Graph
A visual representation of which sessions are blocking others.
What it shows:
- Blocking session → Blocked session relationships
- Chain of blocked processes
- Root blocker identification
How to use it:
- Identify the root cause of blocking
- See cascade effects of blocking
- Prioritize which session to address
Lock Escalation Pattern
What it shows: Lock escalation behavior over time.
Lock escalation:
- Row locks promoted to table locks
- Can cause widespread blocking
- Often indicates suboptimal queries
When to investigate:
- Frequent escalations
- Correlation with blocking
- After query changes
Impact Assessment
What it shows: Business impact of current blocking.
Metrics:
- Number of blocked sessions
- Total wait time
- Affected queries/operations
How to use it:
- Prioritize intervention
- Quantify blocking impact
- Track improvement
Advisory Locks
What it shows: Application-level advisory locks.
Advisory lock types:
- Session-level (released at session end)
- Transaction-level (released at transaction end)
When to investigate:
- Application using advisory locks
- Unexpected lock counts
- Locks not being released
Wait Event Analysis Section
The Wait Event Analysis section shows where PostgreSQL is spending time waiting. This section is collapsed by default — click to expand.
Wait Event Distribution
What it shows: Distribution of wait events by type.
Wait event types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Client | Waiting for client (ClientRead, ClientWrite) |
| Lock | Waiting for heavyweight locks |
| LWLock | Waiting for lightweight locks |
| BufferPin | Waiting for buffer pin |
| IO | Waiting for I/O |
| Activity | Background worker activity |
| Extension | Extension-related waits |
Healthy pattern:
- Mostly Client waits (waiting for queries)
- Low Lock waits
- Minimal IO waits
IO Wait Analysis
What it shows: I/O-related wait events.
IO wait types:
- DataFileRead — Reading data files
- DataFileWrite — Writing data files
- WALWrite — Writing WAL
- WALSync — Syncing WAL
When to investigate:
- High DataFileRead — buffer cache misses
- High WALWrite — heavy write workload
- Any sustained IO waits — storage bottleneck
LWLock Analysis
What it shows: Lightweight lock wait events.
Common LWLocks:
- buffer_content — Buffer access
- WALInsert — WAL insertion
- lock_manager — Lock management
- proc — Process management
When to investigate:
- High buffer_content — buffer contention
- High WALInsert — WAL write contention
- Unusual patterns — configuration issues
Use Cases
Diagnosing Lock Contention
When experiencing slow transactions:
- Check Lock Wait Queue Depth for queueing
- Review Lock Count by Type for lock patterns
- Expand Locks Grid to see specific locks
- Use Blocking Sessions Graph to find blockers
- Check Impact Assessment for severity
Investigating Deadlocks
When deadlocks are occurring:
- Monitor Deadlock Frequency for patterns
- Enable
log_lock_waitsanddeadlock_timeout - Review PostgreSQL logs for deadlock details
- Analyze query patterns causing deadlocks
- Implement consistent lock ordering
-- Enable deadlock logging
ALTER SYSTEM SET deadlock_timeout = '1s';
ALTER SYSTEM SET log_lock_waits = on;
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
Resolving Active Blocking
When you need to resolve blocking immediately:
- Identify blocker in Blocking Sessions Graph
- Check Impact Assessment for severity
- Review blocker's query in Locks Grid
- Decision:
- Wait for completion
- Cancel query:
SELECT pg_cancel_backend(pid) - Terminate session:
SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pid)
-- Cancel a query (graceful)
SELECT pg_cancel_backend(12345);
-- Terminate a session (forceful)
SELECT pg_terminate_backend(12345);
Performance Tuning for Concurrency
To improve concurrent access:
- Review Wait Event Distribution for bottlenecks
- Check LWLock Analysis for internal contention
- Analyze IO Wait Analysis for I/O bottlenecks
- Consider:
- Reducing transaction duration
- Optimizing query access patterns
- Using appropriate isolation levels
- Implementing row-level locking strategies
Monitoring Advisory Locks
If your application uses advisory locks:
- Check Advisory Locks table for current state
- Ensure locks are being released properly
- Monitor for lock accumulation
- Review application lock patterns
Related Metrics
The Locks & Waits section uses these metrics from the Metrics Reference:
| Panel | Primary Metrics |
|---|---|
| Lock Count by Type | pg_locks_count |
| Lock Wait Queue | pg_locks_count (granted=false) |
| Deadlock Frequency | pg_database_stats.deadlocks |
| Locks Grid | pg_lock_detail, pg_backend_info |
| Blocking Sessions | pg_blocking_pids |
| Wait Events | pg_backend_wait_events |
Related Guides
- Performance — Query performance analysis
- Connections — Connection management
- Queries — Query analysis